(Paper) CA-CPT Previous Year Question Paper "June - 2016",Session-2
(Paper) CA-CPT Previous Year Question Paper "June - 2016"
Session - 2
Part A – General Economics
1. Law of demand explains inverse relationship between _______
- a) Price and demand
- b) Demand and Price
- c) Income and demand
- d) Demand and income
2. Which of the following would cause the demand curve for auto mobiles shift to the left?
- a) An increase in price of auto mobiles
- b) An increase in the cost of production of auto mobiles
- c) Increase in buyer’s income
- d) An increase in the interest rate paid to borrow money to pay for auto mobiles
3. What is Net National Product?
- a) The money value of final goods & services produce annually in the year
- b) The money value of annual service generation in the account
- c) The money value of tangible goods produced annually in the economy
- d) The money value of tangible goods available in the economy
4. The law of variable proportions is associated with _____
- a) Short period
- b) Long period
- c) Both short & long periods
- d) Neither short nor long period
5. Balance of payments _____
- a) Current account for goods and services only
- b) A capital account of financial assets only
- c) Official settlement accounts only
- d) All of the above
6. Iso-Quant is also known as:
- a) Product possibilities curve
- b) Production indifference curve
- c) Indifference curve
- d) None of these
7. Which of the following is not a Khariff crop?
- a) Jowar
- b) Maize
- c) Groundnut
- d) Wheat
8. The Philips curve describe the relationship between:
- a) Savings & investment
- b) Marginal tax rate and tax revenue
- c) Unemployment rate and inflation rate
- d) The budget deficit and the trade deficit
9. The concept of ‘entitlements’ was introduced by ______
- a) Pranab Mukharjee
- b) Amartya sen
- c) Manmohan singh
- d) Jagadeesh bhagawathi
10. Micro Economics is the study of ________
- a) Individual parts of economy
- b) Economy as a whole
- c) Choice making .
- d) Development of economy
11. Comparing a monopoly and competitive firm the monopolist will ________
- a) Produce less at lower price
- b) Produce more at lower price
- c) Produce less at higher price
- d) Produce zero at lower price
12. The market price of a good is more than opportunity cost of producing it, then _____
- a) Market price increases in the long run
- b) Producer will increase supply in the long run
- c) Resources will flow outward and there will be a decline in supply
- d) There will not be any change until demand and supply are equal
13. The second glass of lemonade gives lesser satisfaction to a thirsty boy. This is clear case of
- a) Law of variable proportions
- b) Law of diminishing returns
- c) Law of diminishing marginal utility
- d) Law of supply
14. Human capital refers to:
- a) Savings by individuals
- b) Mobilisation of savings
- c) Human skills and abilities
- d) Productive investment
15. Which of the following statement is false ?
- a) Land has indestructible power
- b) Land is passive factor
- c) Capital is nature’s gift
- d) Labour is mobile
16. Among all the states of India _____ has the lowest birth rate
- a) Kerala
- b) Maharastra
- c) Delhi
- d) Uttar Pradesh
17. What is the average calories required in rural areas for measuring poverty?
- a) 2,400 calories per person per day
- b) 2,800 calories per person per day
- c) 2,100 calories per person per day
- d) None of these
18. Multi Dimensional Poverty index is used by ______ to measure poverty
- a) Human Development Report
- b) Tendulkar committee
- c) NSSO
- d) Planning commission of India
19. Which of the following statements defines the density of population?
- a) No. of persons living per unit area
- b) No. of persons living in a country
- c) Change in the no. of inhabitants of a country during a specific per unit of time
- d) Absolute numbers added every year
20. Which of the following statements about repo rate is not correct?
- a) At this rate RBI borrows money from banks for short period
- b) A reduction repo rate helps bank to get money at cheaper rate
- c) An increase in repo rate makes borrowings from RBI expensive
- d) At this rate banks borrow money from RBI
21. Which of the following is broad money?
- a) M1
- b) M2
- c) M3
- d) M4
22. Inflation is _______
- a) Persistent increase in general level of price
- b) Persistent increase in price of individual goods, services & resources
- c) One time increase in general level of price
- d) One time increase in price of individual goods, services & resources
23. Which of the following is not correct?
- a) Direct tax is proportional in nature
- b) An indirect tax is a progressive in nature
- c) A Direct tax cannot be shifted
- d) An indirect tax can be shifted to others
24. Over the years in India cost of tax collection is
- a) Increases
- b) Decreases
- c) Remains unchanged
- d) Indeterminate
25. The ratio of dependents to working age population is called ______
- a) Demographic dividend
- b) Demographic transition
- c) Unemployment ratio
- d) Dependency ratio
26. Special Drawing Rights was created by ______
- a) WTO
- b) World Bank
- c) IMF
- d) UNO
27. India is a _____ economy
- a) Capitalistic
- b) Socialistic
- c) Mixed
- d) Federal
28. Which one of the following expressions is correct for marginal revenue?

29. The vertical difference between TVC and TC is equal to ________
- a) MC
- b) AVC
- c) TFC
- d) None
30. Which of the following is a direct tax?
- a) Personal income tax
- b) Sales tax
- c) Service tax
- d) Excise duties
31. ______ is the best indicator of economic development of any country
- a) Agriculture
- b) Transport
- c) Gross production
- d) Percapita income
32. The price elasticity at mid point of a straight line on demand curve is
- a) = 0
- b) > 1
- c) < 1
- d) = 1
33. If equilibrium is present in a market, then
- a) Quantity demanded is equal to quantity supplied
- b) Quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied
- c) Quantity supplied exceeds quantity supplied
- d) The price of the product will tend to rise
34. Which of the following is not a property of indifference curve?
- a) Indifference curve always touch X-axis
- b) Indifference curve has negative slope
- c) Indifference curve is convex to origin
- d) Indifference curves never intersect each other
35. What happens to marginal cost when average cost increases?
- a) Marginal cost is below average cost
- b) Marginal cost is above average cost
- c) Marginal cost is equal to average variable cost
- d) Marginal cost is equal to average cost
36. Which of the following statement is not correct about the WTO?
- a) WTO came to existence on 1st January, 1995
- b) WTO is main organ for implementing multilateral trade agreements
- c) WTO is legal entity
- d) WTO has lesser scope than its predecessor GATT
37. If the price of a commodity is fixed, then every increase in its sold quantity the total revenue will ______ and the marginal revenue will ____
- a) Increases, also increases
- b) Increases, remain unchanged
- c) Increases, decreases
- d) Remains fixed, increase
38. A discriminating monopolist will charge a higher price in the market in which the demand for its product is
- a) Highly elastic
- b) Relatively elastic
- c) Relatively inelastic
- d) Perfectly elastic
39. Fixed cost curve is normally
- a) Starts from the Origin
- b) ‘U’ shaped
- c) Vertical
- d) Horizontal
40. Find out value of X?
No. of units TU TU
1
30 30
2
27 X
- a) 30
- b) 54
- c) 57
- d) 15
41. What does devaluation of a currency mean?
- a) Decrease in the internal value of money
- b) Decrease in the external value of money
- c) Decrease both in the internal and external values of money
- d) None of these
42. The reason for the kinked demand curve is that
- a) The oligopolist believe that competitors will follow output increases but not output reductions
- b) The oligopolist believe that competitors will follow price increases but not output reductions
- c) The oligopolist believe that competitors will follow price cuts but not price rises
- d) The oligopolist believe that competitors will follow price increases but not output increases
43. A rational producer will produce in the stage in which marginal product is positive and
- a) MP > AP
- b) MP = AP
- c) MP < AP
- d) MP is ‘O’
44. As the price of commodity increases, normally its supply
- a) Decreases
- b) Remain unchanged
- c) Increases
- d) Can’t be determined
45. An economy achieves “productive efficiency” when:
- a) Resources are employed in their most highly valued uses
- b) The best resources are employed
- c) The total number of goods produced is greatest
- d) Goods and services are produced at least cost and no resources are wasted
46. Price elasticity of demand for a product is infinite under
- a) Perfect competition
- b) Monopolistic competition
- c) Monopoly
- d) Oligopoly
47. If a firm under monopoly wants to sell more, its average revenue curve will be a _____ line
- a) Upward sloping
- b) Downward sloping
- c) Vertical
- d) Horizontal
48. The share of which one of the following sectors has increased rapidly in recent years in the GDP of India
- a) Agriculture
- b) Industry
- c) Services
- d) All of the above
49. The marginal rate of substitution ____ as a consumer moves on indifference curve
- a) Increases
- b) Diminishes
- c) Remains unchanged
- d) Becomes zero
50. An indifference curve slopes down towards right since more of one commodity and less of another result in:
- a) Same satisfaction
- b) Greater satisfaction
- c) Maximum satisfaction
- d) Decreasing expenditure
Part B – Quantitative Aptitude
51. The integral part of a logarithm is called ____, and the decimal part of a logarithm is called _____.
- a) Mantissa, Characteristic
- b) Characteristic, Mantissa
- c) Whole, Decimal
- d) None of these
52.

- a) 0
- b) 1
- c) 5
- d) 60
53. If log4 (x2 +x) log4 (x + 1) = 2 then the value of x is
- a) 2
- b) 3
- c) 16
- d) 8
54.

55.

56.
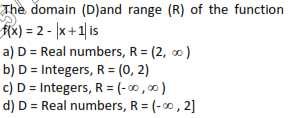
57.

- a) Arithmetic Progression
- b) Geometric Progression
- c) Both A.P & G.P
- d) None of these
58.

59. >A G.P(Geometric Progression)consists of 2n terms. If the sum of the terms occupying the odd places is S1 and that of the terms in even places is S2 , the common ratio of the progression is
![]()
60. If a line passes through the midpoint of the line segment joining the points (-3,-4) & (-5,6) and its slope is 4/5 then the equation of the line is
- a) 4x – 5y + 21 = 0
- b) 4x – 5y + 11 = 0
- c) 5x – 4y + 21 = 0
- d) 5x + 4y + 11 = 0
61.

62.

63

64. Let E1, E2 are two linear equations in two variables x and y. (0, 1) is a solution for both the equations E1 & E2. (2, -1) is a solution of equation E1 only and (-2, -1) is a solution of equation E2 only then E1, E2 are ______.
- a) x = 0, y = 1
- b) 2x – y = -1, 4x + y = 1
- c) x + y = 1, x – y = -1
- d) x + 2y = 2, x + y = 1
65. If difference between the roots of the equation x2 kx + 8 = 0 is 4 then the value of K is
![]()
66.
![]()
- a) 0
- b) 1
- c) -1
- d) Doesn’t exist
67.

68.

69.

70.

71. There are 10 students in a class, including 3 girls. The number of ways arrange them in a row, when any two girls out of them never come together
![]()
72. In how many ways can a selection of 6 out of 4 teachers and 8 students be done so as to include atleast two teachers?
- a) 220
- b) 672
- c) 896
- d) 968
73. The maximum number of points of intersection of 10 circles will be
- a) 2
- b) 20
- c) 90
- d) 180
74. x, y, z together starts a business. If x invests 3 times as much as y invests and y invests two third of what z invests, then the ratio of capitals of x, y, z is _______
- a) 3 : 9 : 2
- b) 6 : 3 : 2
- c) 3 : 6 : 2
- d) 6 : 2 : 3
75. If an amount is kept at Simple Interest, it earns Rs.600 in first 2 years but when kept at Compound Interest it earns at interest of Rs.660 for the same period; then the rate of interest and principle amount respectively are
- a) 20%; Rs.1200
- b) 10%; Rs.1200
- c) 20%; Rs.1500
- d) 10%; Rs.1500
76. Mr. X bought an electronic item for Rs.1000. What would be the future value of the same item after two years, if the value is compounded semiannually at the rate of 22% per annum?
- a) Rs.1488.40
- b) Rs.1518.07
- c) Rs.2008.07
- d) Rs.2200.00
77.

78. Two dice are tossed what is the probability that the total is divisible by 3 or 4.
- a) 20/36
- b) 21/36
- c) 14/36
- d) None
79. If 2 dice are rolled simultaneously then the probability that their sum is neither 3 nor 6 is
- a) 0.5
- b) 0.75
- c) 0.25
- d) 0.80
80. In a game, cards are thoroughly shuffled and distributed equally among four players. What is the probability that a specific player gets all the four kings?

81. A bag contains 4 red and 5 black balls. Another bag contains 5 red, 3 black balls. If one ball is drawn at random from each bag. Then the probability that one red and one black ball drawn is _______.
- a) 12/72
- b) 25/72
- c) 37/72
- d) 13/72
82. If the mean of two numbers is 30 and Geometric Mean is 24 then what will be those two numbers?
- a) 36 and 24
- b) 30 and 30
- c) 48 and 12
- d) None of these
83.

- a) 0.71
- b) 1.39
- c) 1.75
- d) None
84. If same amount is added to or subtracted from all the value of the individual series then the standard deviation and variance both shall be
- a) Changed
- b) Unchanged
- c) Same
- d) None of these
85. The SD of first n natural numbers is ____

86. If mean and coefficient of variation of the marks of n students is 20 and 80 respectively. What will be variance of them
- a) 256
- b) 16
- c) 25
- d) None of these
87. If r = 0.6 then the coefficient of non determination is _____
- a) 0.4
- b) -0.6
- c) 0.36
- d) 0.64
88. If the coefficient of correlation between x and y variables is – 0.90 then what will be the coefficient of determination
- a) 0.10
- b) 0.81
- c) 0.94
- d) None
89. The regression are as follows Regression equation of X on Y : 6X-Y=22 Regression equation of Y on X : 64X-45Y=24 What will be the mean of X and Y?
![]()
90. Purchasing power of money is
- a) Reciprocal of price index number
- b) Equal to price index number
- c) Unequal to price index number
- d) None of these
91. In the year 2010 the monthly salary was Rs.24,000. The consumer price index number was 140 in the year 2010 which rises to 224 in the year 2016. If he has to be rightly compensated what additional monthly salary to be paid to him
- a) Rs. 14,400
- b) Rs. 38,400
- c) Rs. 7,200
- d) None of these
92. The two lines of regression become identical when
- a) r = 1
- b) r = -1
- c) r = 0
- d) a) or b)
93. The suitable index numbers for the comparison of every year is ____
- a) Fixed base index number
- b) Fisher’s ideal index number
- c) Chain base index number
- d) Both a) and c)
94. Data collected on religion from the census reports are
- a) Primary data
- b) Secondary data
- c) Sample data
- d) a) or b)
95. The normal curve is
- a) Positively skewed
- b) Negatively skewed
- c) Symmetrical
- d) All these
96. For a Poisson variate X, P(X=1)=P(X=2). What is the mean of X?
- a) 1
- b) 3/2
- c) 2
- d) 5/2
97. In a discrete random variable follows uniform distribution and assumes only the values 8,9,11,15,18,20. Then P(X < 15) is ____
- a) 1/2
- b) 1/3
- c) 2/3
- d) 2/7
98. A sample may be defined as a part of population is selected with a view to representing in all its ____
- a) Units
- b) Characteristics
- c) Costs
- d) Errors
99. The measure of divergence is ____ as a size of the sample approaches that of the population
- a) More
- b) Less
- c) Same
- d) None
100. A parameter is a characteristic of
- a) Population
- b) Sample
- c) Both a) & b)
d) None of the above
Key – Part A – General Economics
| 1. | A | 11. | C | 21. | C | 31. | D | 41. | B |
| 2. | D | 12. | B | 22. | A | 32. | D | 42. | C |
| 3. | A | 13. | C | 23. | B | 33. | A | 43. | C |
| 4. | A | 14. | C | 24. | A | 34. | A | 44. | C |
| 5. | D | 15. | C | 25. | D | 35. | B | 45. | D |
| 6. | B | 16. | A | 26. | C | 36. | D | 46. | A |
| 7. | D | 17. | A | 27. | C | 37. | B | 47. | B |
| 8. | C | 18. | A | 28. | D | 38. | C | 48. | C |
| 9. | B | 19. | A | 29. | C | 39. | D | 49. | B |
| 10. | C | 20. | A | 30. | A | 40. | C | 50. | A |
Key – Part B – Quantitative Aptitude
| 51. | B | 61. | D | 71. | A | 81. | C | 91. | A |
| 52. | B | 62. | A | 72. | B | 82. | C | 92. | D |
| 53. | C | 63. | A | 73. | C | 83. | B | 93. | C |
| 54. | B | 64. | C | 74. | D | 84. | B | 94. | B |
| 55. | A | 65. | D | 75. | C | 85. | A | 95. | C |
| 56. | D | 66. | D | 76. | B | 86. | A | 96. | C |
| 57. | A | 67. | C | 77. | A | 87. | D | 97. | C |
| 58. | D | 68. | A | 78. | A | 88. | B | 98. | B |
| 59. | C | 69. | B | 79. | D | 89. | C | 99. | B |
| 60. | A | 70. | C | 80. | B | 90. | A | 100. | A |
